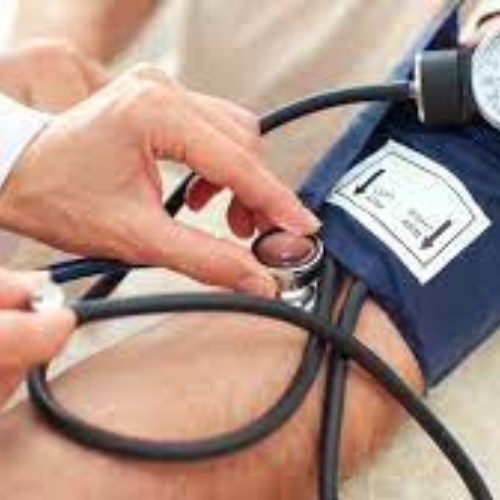
Blood pressure is a critical measure of the force exerted by blood against the walls of the arteries as it circulates through the body. It is an essential indicator of cardiovascular health and plays a significant role in diagnosing and managing various conditions. In this article, we will delve into the concept of blood pressure, its measurement, normal ranges, factors that affect it, and the importance of maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
Blood pressure is typically expressed as two values: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure represents the force exerted on arterial walls when the heart contracts and pumps blood, while the diastolic pressure indicates the pressure on the arterial walls between heartbeats when the heart is at rest. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Normal blood pressure is considered to be around 120/80 mmHg. However, blood pressure can vary among individuals and throughout the day, influenced by factors such as physical activity, stress levels, diet, medications, and overall health. Blood pressure is classified into different ranges:
Normal: Less than 120/80 mmHg
Elevated: 120-129/less than 80 mmHg
Hypertension stage 1: 130-139/80-89 mmHg
Hypertension stage 2: 140/90 mmHg or higher
Hypertensive crisis: Higher than 180/120 mmHg (emergency medical attention required)
Persistent high blood pressure, known as hypertension, is a serious health concern as it strains the heart and damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and other complications. On the other hand, low blood pressure (hypotension) may cause dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood supply to vital organs.
Several factors can affect blood pressure levels. These include:
Lifestyle: Unhealthy habits such as a diet high in sodium and saturated fats, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and physical inactivity can contribute to high blood pressure.
Age: Blood pressure tends to increase with age due to changes in arterial stiffness and the cumulative effects of other risk factors.
Genetics: Family history plays a role in blood pressure. If your parents or close relatives have hypertension, you may be more predisposed to develop it.
Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to higher blood pressure.
Stress: Chronic stress can temporarily elevate blood pressure and, over time, contribute to the development of hypertension.
Managing blood pressure is crucial for overall health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medical interventions are recommended. These include:
Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Reducing sodium intake is particularly important.
Regular exercise: Engaging in aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity can significantly lower blood pressure.
Limiting alcohol and tobacco: Reducing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can improve blood pressure levels and overall cardiovascular health.
Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe antihypertensive medications to help lower blood pressure.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is vital, especially for individuals at higher risk or with existing medical conditions. Home blood pressure monitors are available, but it is essential to follow the proper technique and consult a healthcare professional for accurate interpretation and guidance.
In conclusion, blood pressure is a critical measure of cardiovascular health. Maintaining optimal blood pressure levels through healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and, if necessary, medical interventions is essential for preventing complications and promoting overall well-being. By understanding the factors that influence blood pressure and adopting healthy habits, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.