Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to recurrent episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. It affects people of all ages, and while there is currently no cure, it can be effectively managed with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for asthma.
Causes: The exact cause of asthma is not fully understood, but it is thought to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain triggers can provoke asthma symptoms or exacerbate existing ones. Common triggers include allergens (such as dust mites, pollen, pet dander), respiratory infections, irritants (such as smoke, air pollution, strong odors), physical activity, cold air, and stress.
Symptoms: Asthma symptoms can vary in frequency and severity from person to person. Common symptoms include wheezing (a whistling or squeaky sound during breathing), coughing (particularly at night or in the early morning), chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Symptoms may be intermittent or persistent, and they can range from mild to severe, potentially interfering with daily activities and quality of life.
Diagnosis: To diagnose asthma, a healthcare provider will evaluate an individual’s medical history, conduct a physical examination, and perform lung function tests. Spirometry is a common test used to measure how much air an individual can exhale and how quickly they can do so. In some cases, additional tests such as peak flow measurements, allergy tests, or chest X-rays may be recommended to further evaluate the condition.
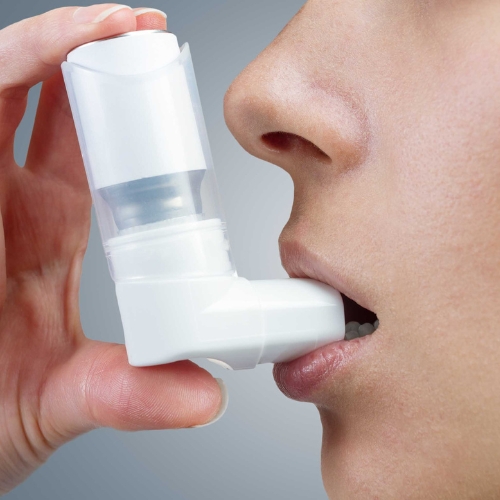
Treatment: The primary goals of asthma treatment are to control symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, and improve overall lung function. Treatment plans are often individualized based on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s response to specific triggers. The two main types of medications used in asthma management are quick-relief medications (bronchodilators) and long-term control medications (corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, long-acting bronchodilators).
Quick-relief medications provide immediate relief during asthma attacks or when symptoms occur. They work by relaxing the muscles around the airways, allowing them to open up and facilitating easier breathing. Long-term control medications are taken regularly to reduce airway inflammation and prevent asthma symptoms. These medications help manage asthma over time and reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
In addition to medications, individuals with asthma are often advised to make lifestyle modifications to help manage their condition effectively. These may include identifying and avoiding triggers, practicing good asthma management techniques (such as using inhalers correctly and regularly monitoring symptoms), maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly (with appropriate precautions), and managing comorbid conditions (such as allergies or acid reflux) that may worsen asthma symptoms.
It is crucial for individuals with asthma to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an asthma action plan. This plan outlines the appropriate use of medications, symptom management strategies, and steps to take during asthma attacks or worsening symptoms. Regular follow-up visits and communication with healthcare providers are essential to assess asthma control, adjust treatment if needed, and ensure that individuals receive proper education and support.
In conclusion, asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies, most individuals with asthma can lead active and fulfilling lives. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for asthma empowers individuals to take control of their condition and work towards achieving optimal asthma control. If you suspect you have asthma or have concerns about your respiratory health, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.