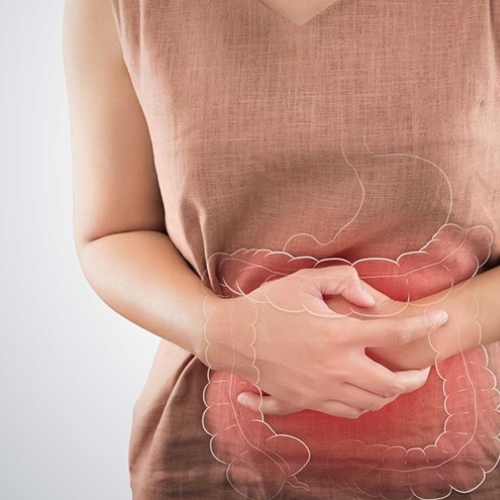
Constipation is a common digestive problem characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stool, or the feeling of incomplete evacuation. It can occur for various reasons and can affect individuals of all ages. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for constipation.
Causes: Several factors can contribute to the development of constipation. Common causes include:
- Inadequate fiber intake: Diets low in fiber can lead to difficulty in passing stool. Fiber adds bulk to the stool and helps promote regular bowel movements.
- Insufficient fluid intake: Not drinking enough water and other fluids can result in hard and dry stool, making it harder to pass.
- Lack of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyles and a lack of regular exercise can slow down the digestive system, leading to constipation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as opioids, antacids containing calcium or aluminum, and some antidepressants, can cause constipation as a side effect.
- Medical conditions: Underlying medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), hypothyroidism, diabetes, and colon disorders, can contribute to chronic constipation.
Symptoms: Common symptoms of constipation include:
- Infrequent bowel movements (less than three times per week)
- Difficulty passing stool
- Hard or lumpy stools
- Straining during bowel movements
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating
Diagnosis: A healthcare provider will typically review an individual’s medical history, conduct a physical examination, and ask about their symptoms. Additional diagnostic tests may be ordered if necessary to identify any underlying causes or rule out more serious conditions. These tests may include blood tests, stool tests, colonoscopy, or imaging studies.
Treatment: The treatment of constipation aims to relieve symptoms, improve bowel movements, and prevent future episodes. Treatment options may include:
- Dietary changes: Increasing fiber intake is often recommended as it helps add bulk to the stool. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Adequate fluid intake is also important to keep stools soft and easy to pass.
- Lifestyle modifications: Regular physical activity and exercise can help stimulate bowel movements. Establishing a regular bathroom routine and allowing sufficient time for bowel movements can also be helpful.
- Medications: Over-the-counter laxatives or stool softeners may be used for short-term relief. However, these should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider and not relied upon for long-term management.
- Addressing underlying conditions: If constipation is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication, addressing and managing that condition may help alleviate symptoms.
Prevention: Preventing constipation involves adopting healthy habits and lifestyle choices. Consider the following preventive measures:
- Eat a fiber-rich diet: Incorporate ample amounts of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your daily meals.
- Stay hydrated: Drink sufficient water and fluids throughout the day to maintain proper hydration.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to promote regular bowel movements and maintain a healthy digestive system.
- Manage stress: High levels of stress can contribute to constipation. Employ stress management techniques such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and hobbies to help alleviate symptoms.
- Establish a regular bathroom routine: Allow yourself ample time for bowel movements and respond to the body’s natural cues.
In conclusion, constipation is a common digestive issue that can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for constipation can help individuals manage and prevent this condition effectively. If constipation persists or is accompanied by severe symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.