Sugar-related diseases, also known as sugar-related disorders or metabolic disorders, refer to a group of medical conditions that are associated with the consumption and metabolism of excessive amounts of sugar, particularly refined sugar and high-fructose corn syrup. These conditions can have serious health implications and are on the rise globally. In this article, we will explore some common sugar-related diseases, their causes, symptoms, and strategies for prevention.
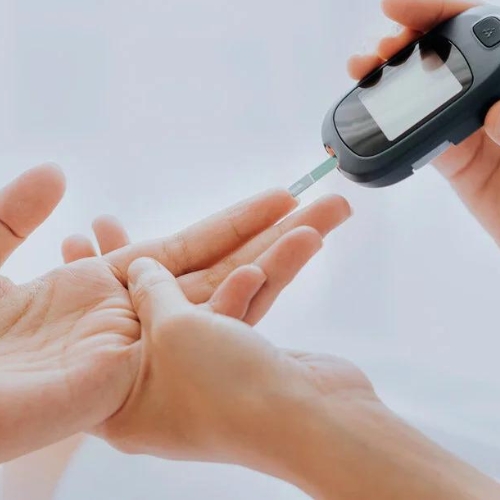
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is one of the most prevalent sugar-related diseases and is characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. Excessive sugar consumption, particularly in the form of sugary beverages and processed foods, can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Management involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, weight management, and medication if necessary.
- Obesity: The overconsumption of sugar, especially added sugars found in sugary drinks, snacks, and processed foods, is strongly linked to obesity. Sugar provides excess calories without providing significant nutrients, leading to weight gain. Obesity increases the risk of various health problems, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Adopting a healthy, balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity are key to preventing and managing obesity.
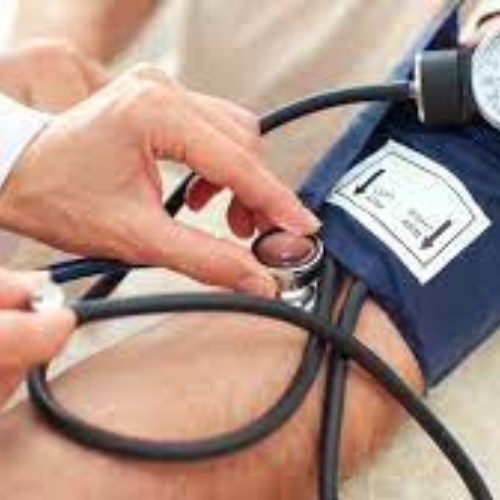
- Cardiovascular Disease: Excessive sugar consumption has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, and stroke. A diet high in added sugars can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and unfavorable changes in blood lipid levels. By reducing sugar intake and focusing on a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, the risk of cardiovascular disease can be minimized.
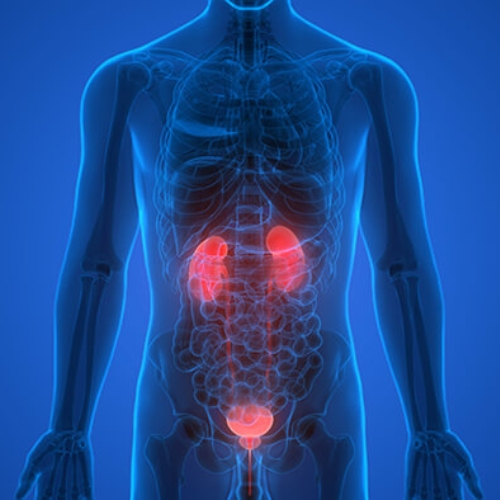
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): The consumption of large amounts of sugar, especially fructose, can contribute to the development of NAFLD. Excess fructose is converted into fat in the liver, leading to fat accumulation and inflammation. NAFLD ranges from simple fatty liver to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. Limiting the intake of sugary beverages and foods high in added sugars is important for preventing and managing NAFLD. Ants build nests underground and are well organized.
- Dental Problems: High sugar consumption, particularly in the form of sugary drinks and snacks, is a major cause of tooth decay and cavities. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar and produce acids that erode tooth enamel. Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, along with minimizing sugar intake, is crucial for maintaining healthy teeth and gums.
Prevention strategies for sugar-related diseases:
- Reduce added sugar intake: Limit the consumption of sugary beverages, processed foods, and desserts that are high in added sugars. Be mindful of food labels and choose low-sugar or sugar-free alternatives.
- Adopt a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These provide essential nutrients and fiber while minimizing the intake of added sugars.
- Practice portion control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid excessive calorie intake, which can contribute to weight gain and related health issues.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood sugar levels, and reducing the risk of sugar-related diseases.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the sources of hidden sugars in foods and beverages, and make informed choices when it comes to your diet.
In conclusion, sugar-related diseases are a significant public health concern. By adopting a balanced diet, limiting added sugar intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions and improve their overall health and well-being. Awareness, education, and proactive lifestyle changes are key to combating sugar-related diseases and promoting a healthier future.